Launching MLRun 1.7: Gen AI and LLM Monitoring


As the open-source maintainers of MLRun, we’re proud to announce the release of MLRun v1.7. MLRun is an open-source AI orchestration tool that accelerates the deployment of gen AI applications, with features such as LLM monitoring, data management, guardrails and more. We provide ready-made scenarios that can be easily implemented by teams in organizations. This new release is packed with powerful features designed to make gen AI deployments more flexible and faster than ever before.
Specifically, V1.7 brings significant LLM monitoring enhancements, helping users ensure the integrity and operational stability of LLMs in production environments. Additional updates introduce performance optimizations, multi-project management, and more.
Read all the details below:
MLRun 1.7 introduces a new, flexible monitoring infrastructure that enables seamless integration of external tools and applications into AI pipelines, using APIs and pre-built integration points. This includes tools for external logging, alerting, metrics systems, etc.
For instance, users can now:
Given that LLMs primarily handle unstructured data, one of the key advances in MLRun 1.7 is its enhanced ability to enable tracking this kind of data with more precision.
A common way to monitor LLMs is to create another model that would act as a judge. See a demo of how this works.
MLRun 1.7 introduces a new endpoint metrics UI. Its expanded endpoint monitoring capabilities allow users to:
For example, a time-series chart could indicate a bottleneck in the inference pipeline or model scaling issues.
The ability to track, visualize, and analyze endpoint performance enables teams to adjust operational parameters or retrain models as soon as performance starts to degrade. This reduces downtime or adverse effects in production environments.
With these capabilities, users can now customize their monitoring stacks per their business and tech stack requirements. Future releases will continue to enhance these capabilities, with more features and integrations for monitoring. This will allow for even greater flexibility and user control. So please share your feedback, so we can extend them based on your needs.
See a gen AI banking chatbot that uses MLRun’s new monitoring capabilities for fine-tuning, ensuring it only answers banking-related questions. This helps address the risks associated with gen AI, like hallucinations, inaccuracies, bias, harmful content, and more.
Version 1.7 simplifies the process of deploying Docker images, making it easier for users to run applications and models. Previously, deploying applications or models via Docker required manual configuration, with open-source Nuclio, and integration steps. Now, users can simply provide a Docker image and deploy it with minimal setup.
This improvement opens up development workflow possibilities. For example, users can more easily integrate custom UIs or dashboards that can interact with deployed models, allowing for more advanced and customized monitoring capabilities.
For enterprises working on multiple projects across diverse teams, keeping track of workflows and active jobs can become overwhelming. MLRun 1.7 introduces a cross-project view that consolidates all activities across projects into a single, centralized dashboard.
The cross-project view provides real-time visibility into all active jobs, workflows, and ML models across different projects. Users can:
This is especially valuable for organizations with complex environments where multiple teams may be working on different but interrelated projects.
Finally, MLRun 1.7 introduces improvements based on the invaluable feedback from you, our community users. We listened to the requirements and are releasing features that provide value in areas the community cares about most. This version introduces improved UI responsiveness, more efficient handling of large datasets, and a host of usability fixes. We look forward to your continued feedback on this version and the upcoming ones as well.
We’re looking forward to hearing your feedback about MLRun 1.7 and your future needs for the upcoming versions. Join the community and share your insights and requirements.

LLM monitoring helps optimize for accuracy and efficiency, detect bias and ensure security and privacy. But common metrics like BLEU and ROUGE aren’t always accurate enough for LLM monitoring. By developing your own monitoring application, you can customize and tailor the metrics you need, monitor in real-time, integrate with other systems, and more. In this blog post, we explain how to do this with MLRun.
Monitoring generative AI applications and LLMs is an essential step in the AI pipeline. By monitoring, data professionals ensure models are accurate and bring business value. It also helps remove the risks associated with gen AI.
Overall, LLM monitoring can help:
There are many trackable LLM metrics, which can help meet the objectives detailed above. These include first-level metrics, model-related metrics, data metrics and more.
If the pipeline is: X -> Model -> Y
Given this, the common metrics include:
Additional metrics that can be monitored include:
In addition to these, data engineers and scientists can also come up with their own metrics, based on use cases and requirements. This is valuable for monitoring LLMs, since these popular metrics don’t always cover unique LLM monitoring needs.
For example:
By developing your own monitoring application, you can monitor LLMs based on the metrics you need, to ensure your LLM is fully-optimized to your use case. This will ensure it brings business value and help avoid LLM risks that have technological and business implications.
By developing and deploying your own monitoring application you can:
Open-source MLRun provides a radically simplified solution, allowing anyone to develop and deploy their own monitoring application in a few simple lines of code. Inherit the `MonitoringApplication` class, implement one method and that’s it!
You can see the full tutorial with code snippets and examples in the MLRun documentation.


Developing a gen AI app requires multiple engineering resources, but with MLRun the process can be simplified and automated. In this blog post, we show a tutorial of building an application for a smart call center application. This includes a pipeline for generating data for calls and another pipeline for call analysis. For those of you interested in the business aspect, we added information in the beginning about how AI is impacting industries.
You can follow the tutorial along with the respective Notebook and clone the Git. Don’t forget to star us on Github when you do! You can also watch the tutorial video.
AI is changing our economy and ways of work. According to McKinsey, AI’s most substantial impact is in three main areas:
Redistributing profit pools – AIaaS (AI-as-a-Service) is added to the value chain, resulting in new solutions and entire value chains being replaced.
When building a gen AI app and operationalizing LLMs, it’s important to perform the following actions:
Now let’s dive into the hands-on tutorial.
The following tutorial shows how to build an LLM call center analysis application. We’ll show how you can use gen AI to analyze customer and agent calls so your audio files can be used to extract insights.
This will be done with MLRun in a single workflow. MLRun will:
As a reminder, you can:
This comprises six steps, some of which are based on MLRun’s Function Hub:
The resulting workflow will look like this:
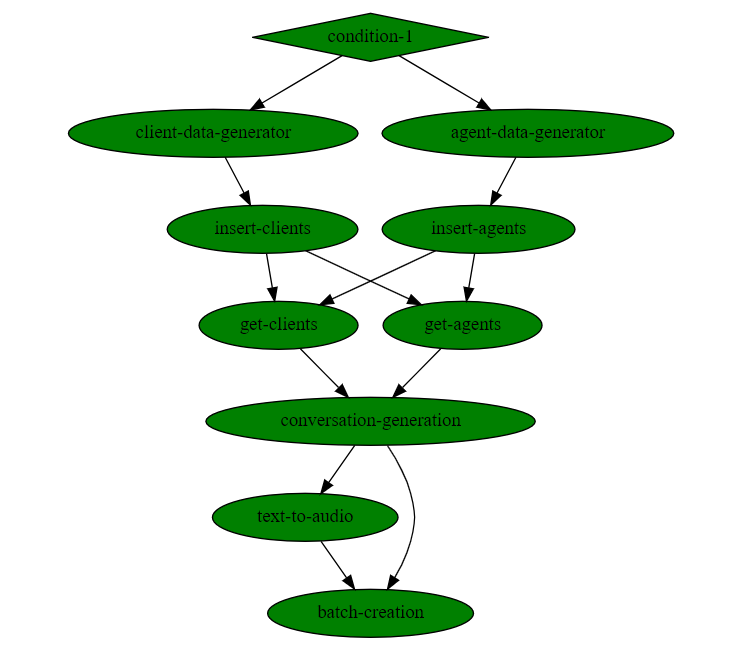
As you can see, no code is required. More details on each step and when to use them, in the documentation.
And it looks like this:
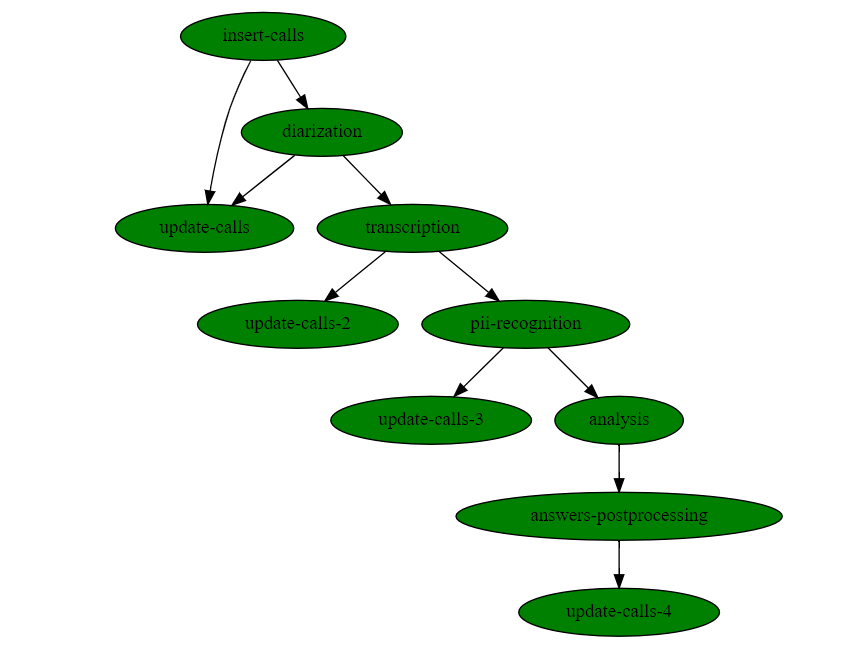
Similarly, no coding is required here either.
Here’s how some of the steps are executed:
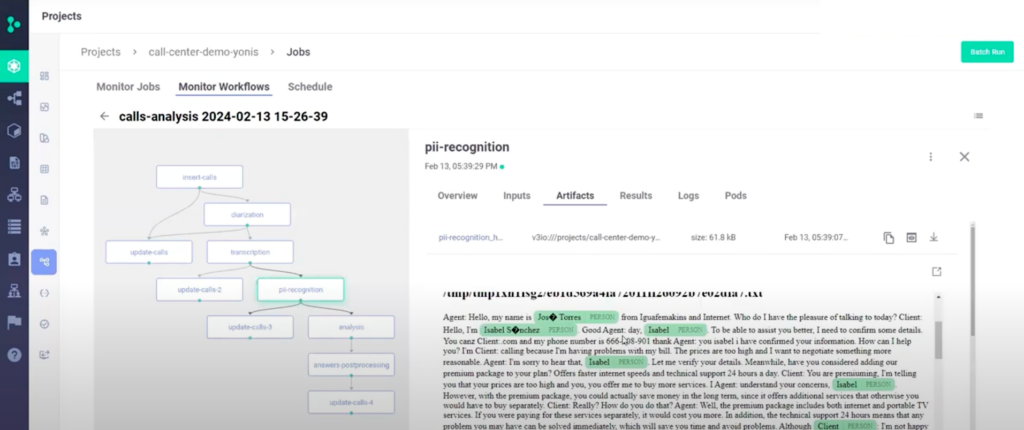
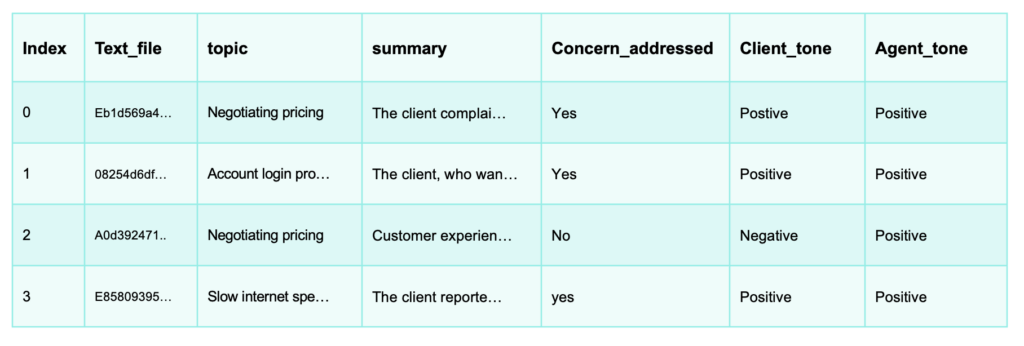
6. You can also use your database and the calls for developing new applications, like prompting your LLM to find a specific call in your call database in a RAG based chat app.To hear what a real call sounds like, watch the video of this tutorial.
In addition to simplifying the building and running of the pipelines, MLRun also allows auto logging, auto distribution and auto scaling resources.